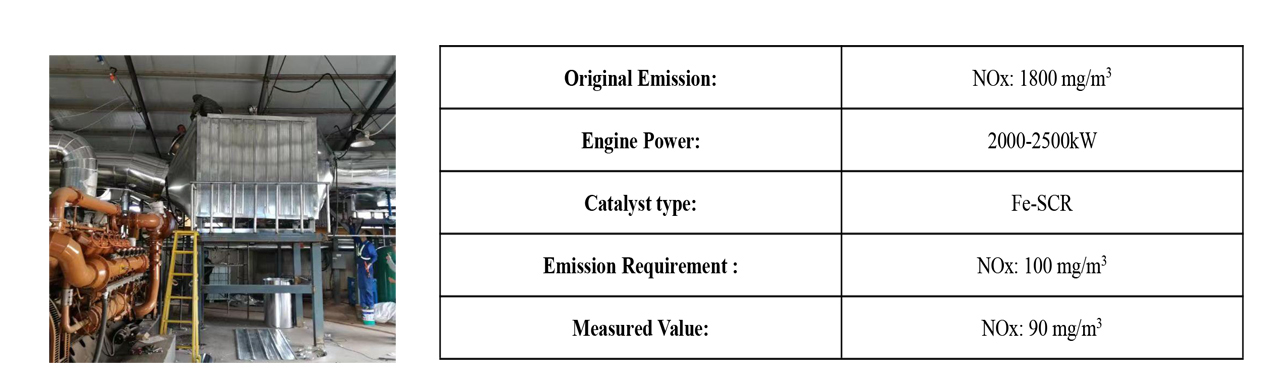
-
High Porosity Ceramic-Coated SCR Catalyst
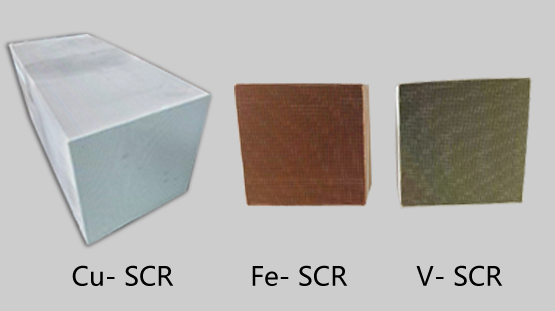
1、Product Overview Catalyst Substrate Specifications:L*W*H 150x150x 100~500mm / 46 or 100 CPSI/ Coating Cu Zeolite SCR or Fe Zeolite SCR or VSCR.
2、Applications:
2.1 Marine Exhaust Gas Aftertreatment Marine Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) catalysts are the core components of ship exhaust aftertreatment systems. They utilize catalytic reactions to convert nitrogen oxides (NOx) emitted by diesel engines into harmless nitrogen gas (N₂) and water vapor (H₂O), effectively complying with the International Maritime Organization (IMO) Tier III emission standards (NOx emission limit ≤3.4 g/kWh). The technical principle involves injecting urea solution or aqueous ammonia as a reducing agent, which selectively reacts with NOx on the catalyst surface to achieve high-efficiency denitrification.2.2 Stationary Power Generation Units Stationary-source Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) catalysts are critical materials for industrial flue gas denitrification systems. They efficiently convert nitrogen oxides (NOx) emitted from fixed pollution sources (e.g., coal-fired or gas-fired power plants) into nitrogen gas (N₂) and water vapor (H₂O), significantly reducing pollutant emissions to meet national ultra-low emission standards (e.g., NOx ≤50 mg/m³) and international environmental regulations. Chinese standards such asTechnical Specification for Testing Flue Gas Denitrification Catalysts in Thermal Power Plants(DL/T 1286-2013) andTesting Methods for Marine SCR Honeycomb Denitrification Catalysts(GB/T 33104-2016) specify testing criteria for catalyst activity, compressive strength (≥1.5 MPa), and chemical durability.
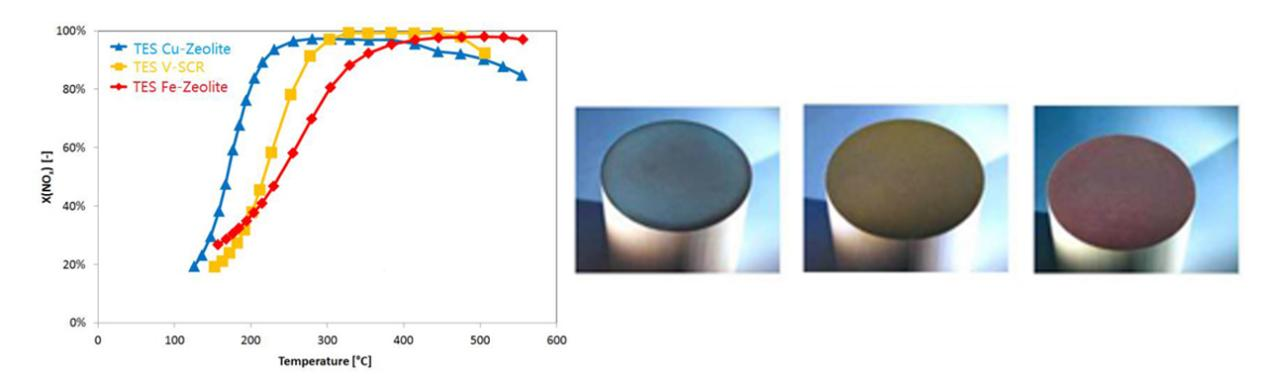
3、Catalytic Efficiency, Conversion Efficiency Diagram, Overview3、Different reaction temperature environments often impose distinct requirements on the active sites of catalysts.
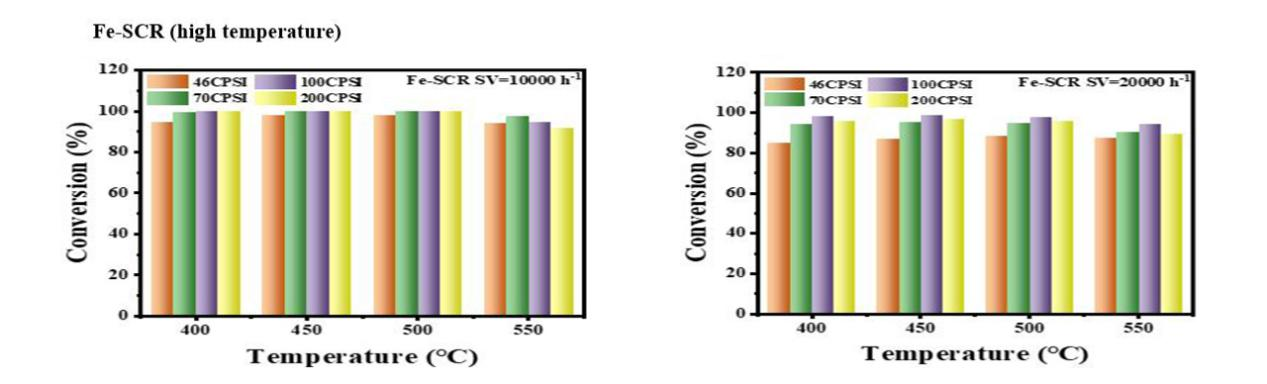
Fe-SCRis primarily designed for high-temperature reaction environments above400 °C. Under a space velocity (SV) of10,000 h⁻¹, the100 CPSIcatalyst achieves nearly100% conversion efficiencywithin the400–500 °Ctemperature range. Even at an elevated SV of20,000 h⁻¹, the100 CPSIcatalyst maintains aconversion efficiency exceeding 97%in the same temperature range (400–500 °C), fully meeting the demands of diverse industrial operating conditions.
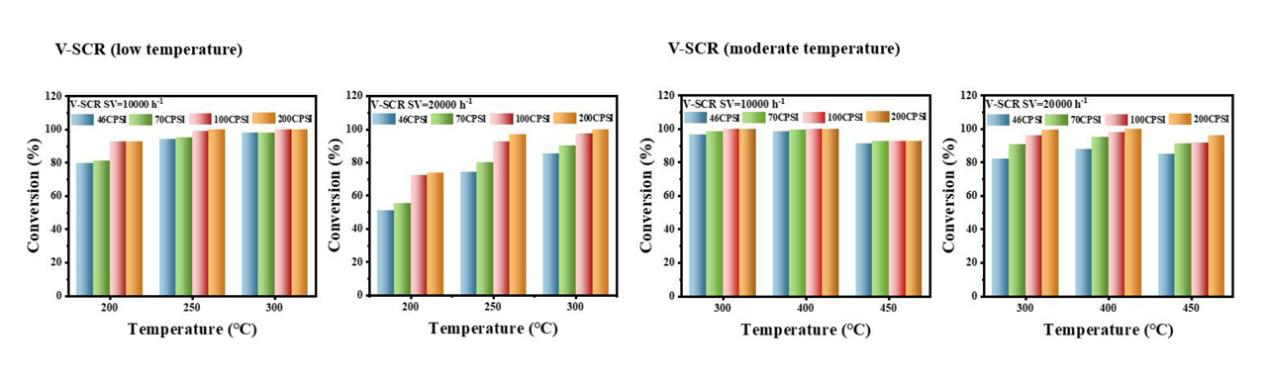
3.2 V-SCRis engineered for low- to medium-temperature reaction environments, operating within a200–450 °Crange. Higher CPSI (cells per square inch) enhances the catalyst's conversion efficiency. At SV = 10,000 h⁻¹:
Achieves>90% conversion efficiencyeven at low temperatures (200 °C).
Deliversnear 100% efficiencywithin the250–400 °Crange. At SV = 20,000 h⁻¹:
Deliversnear 100% efficiencywithin the250–400 °Crange. At SV = 20,000 h⁻¹:
Sustainsnear 100% efficiencyin the250–400 °Crange.
This performance ensures robust adaptability to fluctuating industrial conditions while meeting stringent emission control requirements.
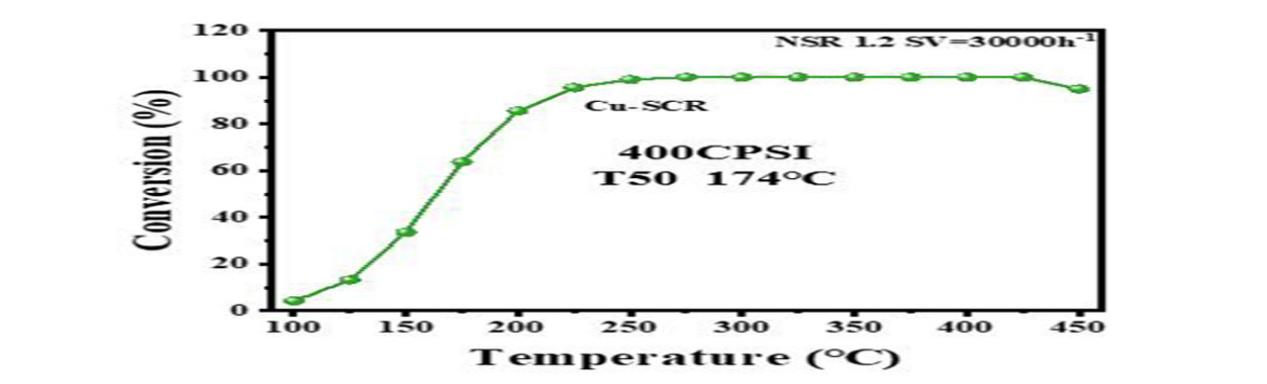
3.3 Cu-SCRis specifically designed for low-temperature reaction environments within the180–350 °Crange. Under a space velocity (SV) of30,000 h⁻¹, the400 CPSIcatalyst achieves>50% conversion efficiencyat temperatures as low as174 °Cand deliversnear 100% efficiencyin the250–400 °Crange.
Key Considerations:
Sub-180 °C Operation:
While conversion is possible below 180 °C, urea hydrolysis does not occur, and crystallization risks increase in low-temperature conditions.
High-Temperature Limitations:
Efficiency declines at elevated temperatures, making Cu-SCR ideal for applications requiring optimized performance in low- to moderate-temperature ranges.
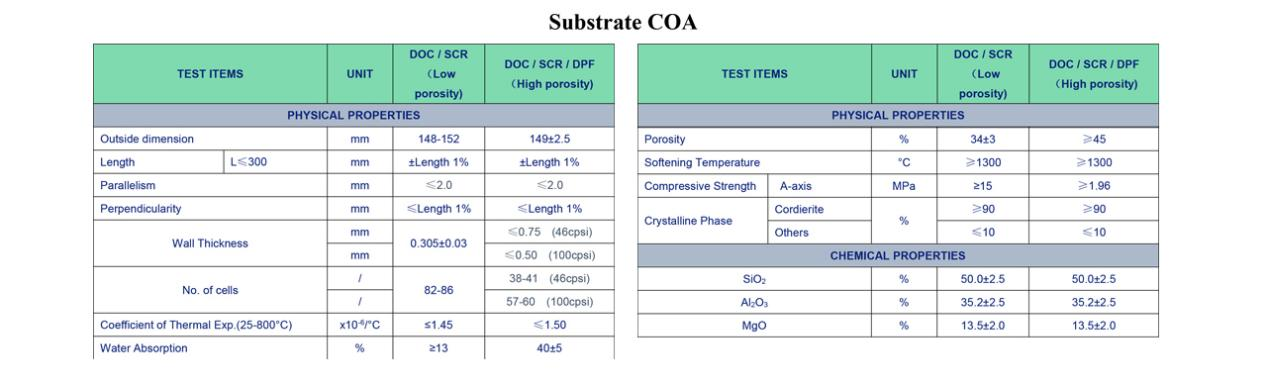
4、Substrate COA
5、Case