-
CDPF (Catalytic Diesel Particle Filter)
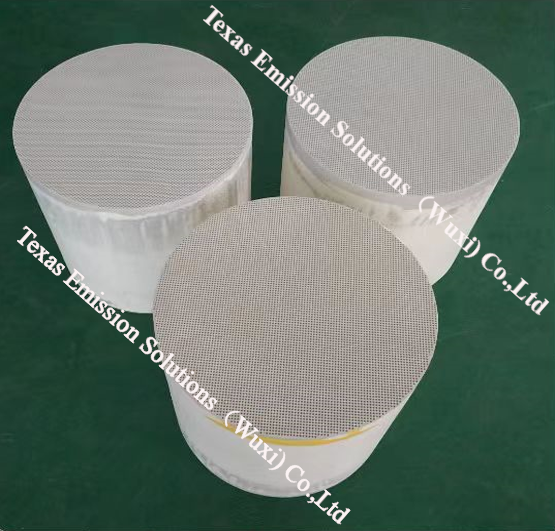
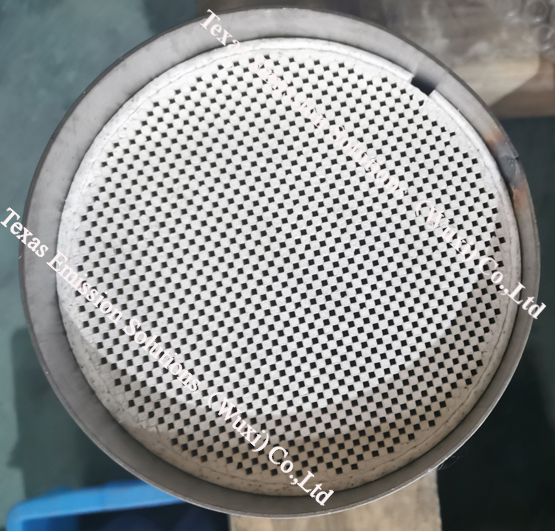


A diesel particulate filter (DPF) is a device designed to capture particulate matter emitted by diesel vehicles, including dust and smoke, to reduce pollution emissions. The DPF is a filter installed in the exhaust system of diesel vehicles. As exhaust gases pass through the filter, the particulate matter is trapped in the filter's pores, preventing it from entering the atmosphere. Over time, the accumulation of particulate matter can cause the filter to become clogged and require cleaning or replacement. The DPF is an essential environmental device and is widely used in modern diesel vehicles. Many industrialized countries and regions have laws mandating the use of DPFs to reduce emissions.
The fundamental principle of the DPF is to reduce emissions by filtering and capturing particulate matter from diesel vehicle exhaust. Exhaust gas from the diesel vehicle's exhaust pipe is directed into the DPF filter. The filter walls are covered with high surface area nano-particle materials that effectively capture particulate matter from the exhaust gas, producing CO2 and extending the DPF's lifespan. As exhaust gas flows through the DPF, particulate matter is captured in the filter walls' pores, and the exhaust gas flows out through the filter's gaps. With time, particulate matter buildup can cause the filter to become blocked, leading to reduced vehicle performance and even failure. Regular cleaning and maintenance of the DPF is necessary to ensure its effective operation. Cleaning methods such as thermal regeneration cleaning, chemical cleaning, or mechanical cleaning can be used. Additionally, diesel vehicle owners should adhere to specific guidelines, such as avoiding high-speed driving with the engine turned off, to prolong the DPF's lifespan.
The coating of catalysts on the DPF's walls is critical to the CDPF (Coated DPF) technology and process. The catalyst must be uniformly coated on the ceramic carrier walls, preventing the coating from becoming too thick and blocking the micro-pores inside the DPF. This blockage can cause the entire exhaust aftertreatment system's back pressure to exceed the standard.
The catalyst coating on the DPF wall will convert NO, which has already reacted with carbon, back into NO2:
1.NO + ½O2 → NO2;It then promotes another reaction with carbon to produce CO2:
2.[C] + 2NO2 → CO2 + 2NO
The TES CDPF utilizes cutting-edge nanomaterial technology to achieve a balance between product durability and cost-effectiveness, resulting in a significantly superior lifespan and performance of the diesel particulate filter (DPF) when compared to our competitors. Over the course of the past three years, we have successfully sold an estimated annual range of 5,000 to 15,000 DPFs to our valued customers, all without encountering any post-sale product issues.