-
SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction)
The SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) system and ASC (Ammonia Slip Catalyst) are two essential components in the exhaust aftertreatment system of diesel vehicles. The SCR system's primary function is to reduce nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions from diesel engines, while the ASC system is used to capture and reduce ammonia (NH3) slip from the SCR system, which is an essential step in achieving compliance with stringent emissions regulations.
The SCR system works by injecting a urea-based solution, commonly known as diesel exhaust fluid (DEF), into the exhaust stream, which reacts with a catalyst to break down NOx into harmless nitrogen (N2) and water (H2O).
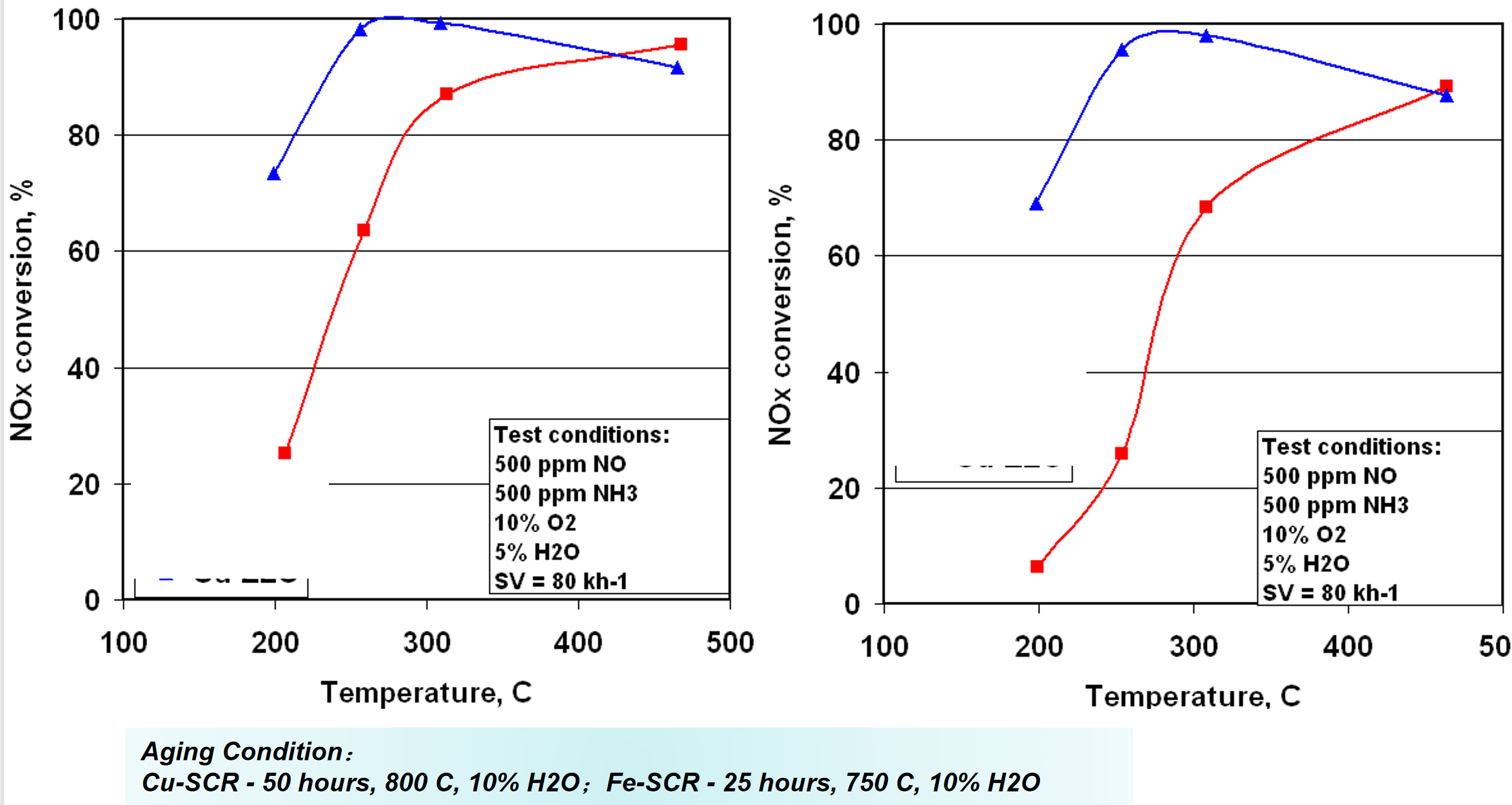
Commercial diesel engine SCR catalysts mainly include V-SCR catalysts and molecular sieve SCR catalysts. The V-SCR catalyst can meet the Europe IV and V emission standards for diesel engines on the road; Molecular sieve SCR catalysts are also divided into Cu-SCR and Fe-SCR, mainly used for road diesel engines with Europe VI and non road diesel engines with Europe IV and above emission standards.
The ASC system is designed to capture and reduce ammonia slip by utilizing a specialized catalyst that reacts with the excess ammonia to convert it into harmless nitrogen and water.
Chemical reactions in the SCR and ASC systems are:
*. SCR: (NH2)2CO+H2O→2NH3+CO2 NO + NO2 + 2NH3 → 2N2 + 3H2O
*. ASC: 4NH3 + 3O2 → 2N2 + 6H2O
TES's SCR and ASC products are designed and manufactured to the highest industry standards, ensuring reliable and efficient performance for our customers. Our SCR systems are optimized for maximum NOx reduction and comply with the strictest emission regulations. The integration of ASC technology in our SCR systems further enhances the overall performance and durability, making them a cost-effective solution for diesel engine emission control. With years of experience and a commitment to innovation, TES offers reliable and high-performance SCR and ASC solutions for a wide range of diesel applications.



CU-SCR & FE-SCR Application Line